Understanding Umbilical Hernias in Adults
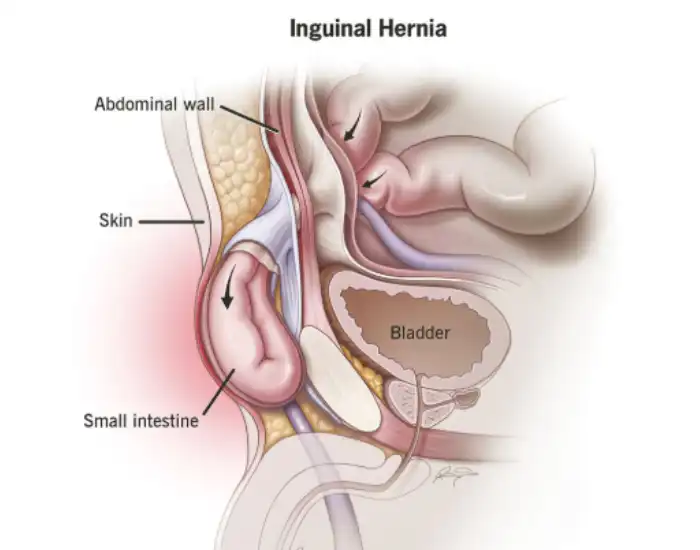
An umbilical hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine or fatty tissue, pushes through a weakened area of the abdominal wall near the navel (umbilicus). While umbilical hernias are often associated with infants, they can develop in adults due to factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure or weaken the abdominal wall.
Common contributors include:
-
Pregnancy: Increased pressure on the abdominal wall during pregnancy can lead to hernia formation, especially in women with multiple pregnancies.
-
Obesity or rapid weight gain: Excess abdominal fat strains the abdominal wall.
-
Chronic coughing or heavy lifting: Repetitive strain may gradually cause weakness.
-
Previous abdominal surgery: Scars or tissue weakness can predispose patients to hernias.
-
Age-related tissue weakening: Natural loss of muscle tone can make the abdominal wall more susceptible.
Unlike some childhood hernias that may resolve on their own, adult umbilical hernias rarely close spontaneously and often require careful evaluation.
Recognizing Symptoms of Umbilical Hernia in Adults
Umbilical hernias in adults can be subtle or quite noticeable. Symptoms may include:
-
Visible bulge or swelling at or near the belly button, especially when standing, coughing, or straining
-
Discomfort or aching pain in the abdominal area
-
Pressure or heaviness around the navel
-
Occasional nausea or digestive changes if the intestine is involved
-
Tenderness or redness in more severe or complicated cases
Many patients report that the bulge reduces or disappears when lying down, which can make the condition easy to overlook. However, persistent bulges, discomfort, or changes in size require medical evaluation.
When Umbilical Hernias Require Urgent Attention
While most adult umbilical hernias are manageable, certain symptoms signal the need for immediate medical care, including:
-
Sudden, intense abdominal pain
-
Redness, warmth, or tenderness around the hernia
-
Nausea, vomiting, or inability to pass gas
-
Bulge that cannot be gently pushed back in
These signs may indicate incarceration (trapped tissue) or strangulation (compromised blood flow), both of which are surgical emergencies. Prompt intervention is crucial to prevent serious complications.
Evaluating an Umbilical Hernia
Evaluation begins with a physical examination, where a surgeon will assess:
-
The size, location, and reducibility of the bulge
-
Tenderness or signs of inflammation
-
Changes with standing, coughing, or straining
In some cases, imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans are used to clarify the contents of the hernia sac and detect any associated complications. Accurate assessment guides the most effective treatment plan.
Treatment Pathways: Non-Surgical vs. Surgical
Treatment depends on hernia size, symptoms, and patient health.
Non-Surgical Management
For small, minimally symptomatic hernias, a conservative approach may be appropriate:
-
Watchful waiting: Monitoring the hernia for changes while avoiding heavy lifting or straining
-
Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, strengthening abdominal muscles, and managing chronic cough or constipation
-
Supportive belts or trusses: These provide temporary relief but do not repair the hernia
Non-surgical approaches can be safe for select patients, but they do not eliminate the hernia or prevent eventual growth or complications.
Surgical Repair
Surgery is the definitive treatment for most adult umbilical hernias. Modern surgical techniques focus on minimizing discomfort, promoting faster recovery, and reducing recurrence:
-
Open repair: A small incision is made over the navel, the protruding tissue is returned to the abdominal cavity, and the wall is reinforced with sutures or mesh.
-
Laparoscopic repair: Minimally invasive technique using small incisions and a camera to repair the hernia, offering quicker recovery and less post-operative pain.
-
Robotic-assisted repair: Advanced robotic systems provide enhanced precision and visualization, allowing meticulous reinforcement of the abdominal wall with smaller incisions and faster return to normal activities.
The choice of technique depends on hernia size, patient anatomy, and surgeon expertise.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery varies depending on the procedure and overall health. Key considerations include:
-
Gradual return to light activities within days
-
Avoidance of heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for 4–6 weeks
-
Monitoring for signs of infection, swelling, or recurrence
-
Following specific dietary recommendations if bowel involvement was present
Patients often experience significant improvement in comfort and quality of life once the hernia is repaired.
Lifestyle Considerations to Support Long-Term Health
Even after successful repair, certain practices can help prevent recurrence and maintain abdominal health:
-
Maintain a healthy body weight
-
Avoid sudden heavy lifting or strain
-
Engage in core-strengthening exercises with guidance
-
Manage chronic cough or respiratory conditions
-
Treat constipation promptly to avoid straining
Lifestyle adjustments complement surgical repair and promote overall abdominal wellness.
Choosing the Right Specialist
Adult umbilical hernias are best managed by a general surgeon with experience in minimally invasive and robotic techniques. When searching for a hernia surgeon near me, patients should consider specialists who:
-
Are board-certified in general surgery
-
Have experience with laparoscopic and robotic hernia repair
-
Provide personalized treatment plans and clear guidance
-
Offer comprehensive post-operative care and follow-up
Selecting an experienced surgeon improves outcomes, minimizes complications, and ensures a safe, effective recovery.
Final Thoughts
Umbilical hernias in adults are common, especially after pregnancy, weight changes, or abdominal strain. While small, asymptomatic hernias may be monitored, most adults benefit from timely evaluation and surgical repair. Understanding the symptoms, risks, and modern treatment options, including robotic-assisted surgery, empowers patients to make informed decisions and regain confidence in their health.
Prompt consultation with a qualified general surgeon provides individualized recommendations, ensuring optimal care and a smooth recovery. Recognizing the signs early can prevent complications and restore comfort, mobility, and peace of mind.
If you notice a bulge near your belly button, experience discomfort, or are wondering “does umbilical hernia need surgery,” consult a general surgeon promptly. Surgical Associates of Southern Texas offers advanced care, including robotic hernia repair, tailored treatment plans, and comprehensive post-operative support. Searching for a hernia surgeon in Houston, Katy, or Sugar Land? Schedule a consultation today to take the first step toward safe, effective treatment.
Medical Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider regarding any medical concerns or before starting any treatment.