Noticing a bulge or discomfort in the abdominal area, especially after a previous surgery, can be unsettling. Many adults wonder if it’s something minor or a more significant concern like a ventral hernia. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and modern repair options can guide patients toward informed decisions. Questions such as “what is ventral hernia?” or “how long does ventral hernia repair recovery take?” are common, reflecting both curiosity and concern. By learning the key signs and treatment approaches, patients can take proactive steps to protect their health and regain comfort.
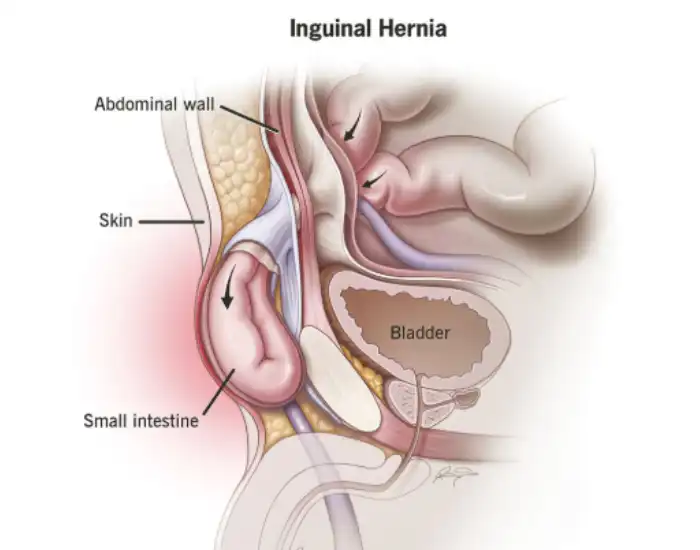
A ventral hernia occurs when tissue or part of the intestine pushes through a weakened spot in the abdominal wall, often near prior surgical scars. Unlike small hernias that may go unnoticed, a ventral hernia can gradually enlarge, cause discomfort, or even lead to complications if untreated. Understanding the condition early ensures timely evaluation and access to advanced surgical options.
What Is a Ventral Hernia?
A ventral hernia is a protrusion of abdominal tissue through a weakness in the abdominal wall. While hernias can develop in various locations, ventral hernias typically occur at the site of previous surgical incisions (incisional hernias) or in areas weakened by injury, infection, or aging.
Key factors contributing to ventral hernia formation include:
-
Previous abdominal surgeries, such as appendectomy, cesarean section, or laparotomy
-
Weakening of the abdominal wall over time due to age or chronic conditions
-
Obesity or rapid weight gain that increases abdominal pressure
-
Chronic coughing, straining, or constipation
-
Smoking or poor wound healing
Identifying the risk factors is crucial, as it can help patients prevent recurrence after surgical repair and maintain long-term abdominal health.
Common Symptoms of a Ventral Hernia
Symptoms of a ventral hernia may vary depending on size, location, and severity. Patients often notice:
-
Visible bulge at or near a previous surgical scar or midline of the abdomen
-
Pain or discomfort when standing, lifting, or engaging in physical activity
-
Pressure or heaviness in the abdominal wall
-
Digestive changes, including bloating or occasional nausea
-
Tenderness or redness in more advanced or complicated cases
Some patients have small ventral hernias that are painless and only detected during routine examinations. However, even minor hernias should be monitored closely to avoid complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many ventral hernias can be evaluated and repaired electively, some situations require urgent care:
-
Sudden, intense abdominal pain
-
Redness, warmth, or swelling over the hernia
-
Nausea, vomiting, or inability to pass gas
-
Bulge that cannot be pushed back in
These signs may indicate incarceration or strangulation, where trapped tissue loses blood supply. Immediate surgical intervention is critical to prevent life-threatening complications.
Diagnosing a Ventral Hernia
Evaluation of a ventral hernia typically begins with a thorough physical exam. A surgeon may examine:
-
The size, location, and reducibility of the bulge
-
Tenderness or signs of inflammation
-
Changes with standing, coughing, or straining
Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scan, can be helpful for confirming the diagnosis, particularly in patients with obesity or complex abdominal anatomy. Accurate diagnosis informs the best approach to treatment.
Treatment Options for Ventral Hernia
Management of a ventral hernia depends on symptoms, hernia size, and patient health.
Non-Surgical Management
For small or minimally symptomatic hernias:
-
Watchful waiting: Monitoring the hernia for changes while avoiding heavy lifting or straining
-
Lifestyle adjustments: Maintaining a healthy weight, managing cough, and treating constipation
-
Supportive garments: Hernia belts or trusses can provide temporary relief but do not repair the hernia
Non-surgical approaches can be safe for select patients, but they do not prevent eventual enlargement or complications.
Surgical Repair
Surgery is the definitive treatment for a ventral hernia, especially when symptoms affect daily life or the hernia enlarges. Modern repair methods focus on minimizing discomfort, reducing recurrence, and promoting faster recovery:
-
Open ventral hernia repair: A larger incision allows direct access to the hernia, with reinforcement using sutures or mesh.
-
Laparoscopic ventral hernia repair: Minimally invasive technique using small incisions and a camera to repair the hernia. Benefits include faster recovery, smaller scars, and less post-operative pain.
-
Robotic-assisted ventral hernia repair: Advanced robotic systems provide precise repair, improved visualization, and enhanced abdominal wall reconstruction.
The choice of technique depends on hernia complexity, size, patient health, and surgeon expertise.
Recovery After Ventral Hernia Surgery
Recovery timelines vary, but general guidance includes:
-
Returning to light activities within a few days
-
Avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for 4–6 weeks
-
Following post-operative instructions to minimize infection or recurrence risk
-
Monitoring for swelling, pain, or bulge recurrence
Patients undergoing laparoscopic or robotic ventral hernia repair often experience faster recovery, reduced discomfort, and smaller scars compared to traditional open surgery.
Lifestyle Considerations Post-Repair
Supporting abdominal health after ventral hernia repair helps prevent recurrence:
-
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce abdominal pressure
-
Engage in guided core-strengthening exercises
-
Avoid heavy lifting and sudden strain on the abdominal wall
-
Manage chronic coughing or respiratory conditions
-
Treat constipation promptly to reduce straining
Lifestyle modifications complement surgical repair and support long-term wellness.
Choosing the Right Specialist for Ventral Hernia
A general surgeon experienced in abdominal wall reconstruction is best suited to manage a ventral hernia. Patients searching for a hernia surgeon near me should look for surgeons who:
-
Are board-certified in general surgery
-
Have expertise in laparoscopic and robotic ventral hernia repair
-
Provide individualized treatment plans and clear explanations
-
Offer comprehensive post-operative support
Selecting a skilled surgeon ensures optimal outcomes, reduces complication risks, and improves patient confidence throughout recovery.
Cost Considerations for Ventral Hernia Surgery
Understanding ventral hernia surgery cost helps patients plan and prepare for treatment. Costs vary based on:
-
Surgical technique (open, laparoscopic, robotic)
-
Facility fees and hospital charges
-
Complexity and size of the hernia
-
Pre- and post-operative care
Insurance often covers medically necessary repairs, but patients should confirm coverage and discuss options with their surgical team.
Final Thoughts
A ventral hernia is a common condition that can arise after abdominal surgery, weight changes, or chronic strain. Recognizing symptoms, understanding treatment options, and consulting a qualified surgeon early can prevent complications and restore comfort. Modern surgical approaches, including minimally invasive and robotic techniques, offer faster recovery, less discomfort, and durable results.
Patients who notice a bulge, experience abdominal discomfort, or have concerns about a previous surgical site should seek evaluation from an experienced general surgeon to discuss ventral hernia repair options tailored to their needs.
If you suspect a ventral hernia or are exploring repair options, consult a general surgeon with expertise in minimally invasive and robotic hernia surgery. Surgical Associates of Southern Texas provides advanced care, personalized treatment plans, and comprehensive post-operative support. Searching for a hernia surgeon near me in Houston, Katy, or Sugar Land? Schedule a consultation today to learn about ventral hernia repair recovery and the best approach for your health.
Medical Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment recommendations.